Monitoring Solution using a TimeSeries Database exporting Infra Metrics (Part 2)

What is Kafka ?
Apache Kafka is a distributed data store optimized for ingesting and processing streaming data in real-time. Streaming data is data that is continuously generated by thousands of data sources, which typically send the data records in simultaneously. A streaming platform needs to handle this constant influx of data, and process the data sequentially and incrementally.
Kafka provides three main functions to its users:
· Publish and subscribe to streams of records
· Effectively store streams of records in the order in which records were generated
· Process streams of records in real time
Kafka is primarily used to build real-time streaming data pipelines and applications that adapt to the data streams. It combines messaging, storage, and stream processing to allow storage and analysis of both historical and real-time data.
Kafka use cases
As an example, a social media application might model Kafka topics for posts, likes, and comments. The application incorporates producers and consumers that subscribe to those Kafka topics. When a user of the app publishes a post, or comments, that data is sent (produced) to the associated topic. When a user goes to the social media site or clicks to pull up a particular page, a Kafka consumer reads from the associated topic and this data is rendered on the web page.
Architecture of Apache Kafka

These are four main parts in a Kafka system:
- Broker: Handles all requests from clients (produce, consume, and metadata) and keeps data replicated within the cluster. There can be one or more brokers in a cluster.
- Zookeeper: Keeps the state of the cluster (brokers, topics, users).
- Producer: Sends records to a broker.
- Consumer: Consumes batches of records from the broker.
Workflow of Apache Kafka
1.Producers send message to a topic at regular intervals.
2.Kafka broker stores all messages in the partitions configured for that particular topic. It ensures the messages are equally shared between partitions. If the producer sends two messages and there are two partitions, Kafka will store one message in the first partition and the second message in the second partition.
3.Consumer subscribes to a specific topic.
4.Once the consumer subscribes to a topic, Kafka will provide the current offset of the topic to the consumer and also saves the offset in the Zookeeper ensemble.
5.Consumer will request the Kafka in a regular interval for new messages.
6.Once Kafka receives the messages from producers, it forwards these messages to the consumers.
7.Consumer will receive the message and process it.
8.Once the messages are processed, consumer will send an acknowledgement to the Kafka broker.
9.Once Kafka receives an acknowledgement, it changes the offset to the new value and updates it in the Zookeeper. Since offsets are maintained in the Zookeeper, the consumer can read next message correctly even during server outrages.
What is Confluent Platform?
Confluent Platform is a full-scale data streaming platform that enables you to easily access, store, and manage data as continuous, real-time streams. Confluent expands the benefits of Kafka with enterprise-grade features while removing the burden of Kafka management or monitoring.
What is Confluent Used For?
Confluent Platform lets you focus on how to derive business value from your data rather than worrying about the underlying mechanics, such as how data is being transported or integrated between disparate systems. Specifically, Confluent Platform simplifies connecting data sources to Kafka, building streaming applications, as well as securing, monitoring, and managing your Kafka infrastructure. Today, Confluent Platform is used for a wide array of use cases across numerous industries, from financial services, omnichannel retail, and autonomous cars, to fraud detection, microservices, and IoT.

Confluent Kafka vs. Apache Kafka: Terminologies
Confluent Kafka is mainly a data streaming platform consisting of most of the Kafka features and a few other things.
Its main objective is not limited to provide a pub-sub platform only but also to provide data storage and processing capabilities.
While on the other hand, Apache Kafka is a pub-sub platform that helps companies transform their data co-relation practices.
Confluent Kafka vs. Apache Kafka: Technology Type
While both platforms fall under big data technologies, they are classified into different categories. Confluent Kafka falls under the data processing category in the big data.
On the other hand, Apache Kafka falls under the data operations category as it is a message queuing system.
Confluent Kafka vs. Apache Kafka: Pros and Cons
Confluent Kafka Pros
· It has almost all the attributes of Kafka and some extra attributes as well.
· It streamlines the admin operations procedures with much ease.
· It takes the burden of worrying about data relaying, off the data managers.
Confluent Kaka Cons
· Confluent Kafka is created by using Apache Kafka, and hence the scope of tweaking it further is limited.
· Confluent Kafka’s fault-tolerant capabilities may be questioned in some cases.
Apache Kafka Pros
· Apache Kafka is an open-source platform.
· It allows you to have the flexibility and features to tweak the code as per your requirements.
· It is known for its fault tolerance and durability.
· It is easily accessible and gives you real-time feedback.
Apache Kafka Cons
· It is only a pub-sub platform and doesn’t have the entire data processing and data operations tools.
· In some cases, if the workload goes too high, it tends to work an awry manner.
· You cannot use the point-to-point and request/reply messages in Apache Kafka.
Confluent Kafka Components
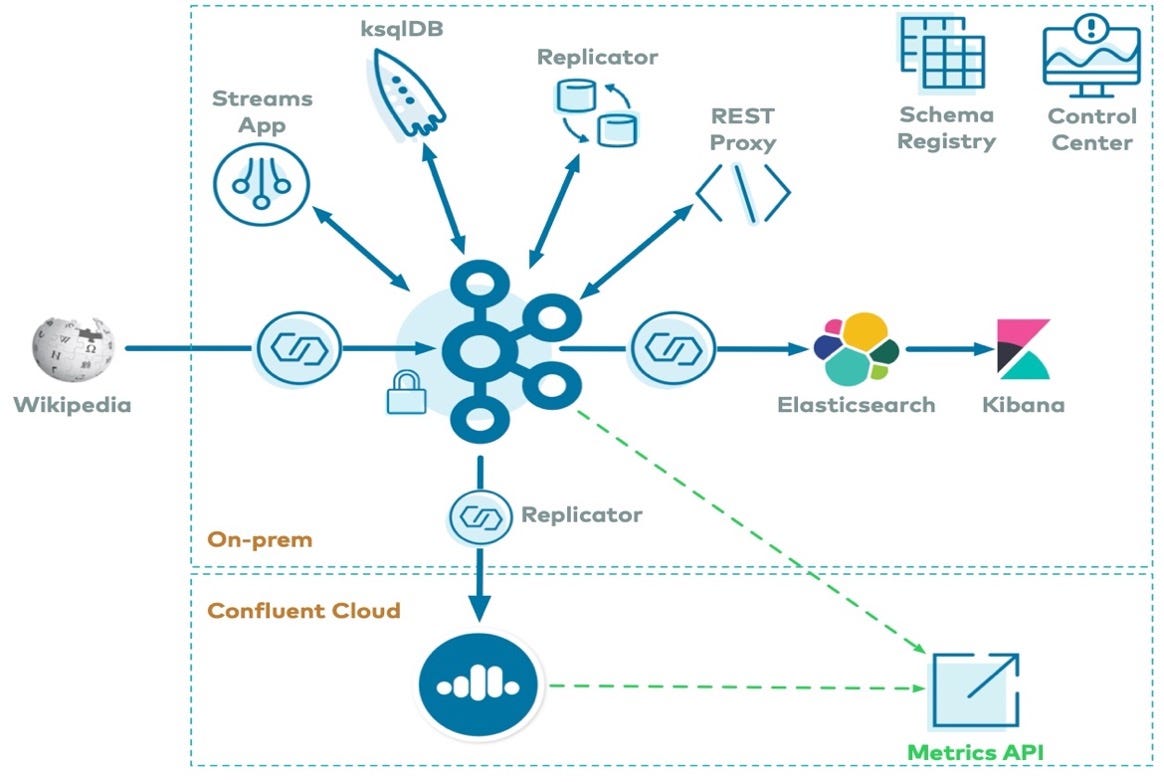
Zookeeper : It is primarily used to track the status of nodes in the Kafka cluster and maintain a list of Kafka topics and messages. It is used to store persistent cluster metadata.
Kafka : It is a full-scale streaming platform, capable of not only publish-and-subscribe, but also the storage and processing of data within the stream.
Schema Registry : It is a standalone server process that runs on a machine external to the Kafka brokers. Its job is to maintain a database of all of the schemas that have been written into topics in the cluster for which it is responsible.
Kafka Connect : It is a tool for scalably and reliably streaming data between Apache Kafka and other data systems. It makes it simple to quickly define connectors that move large data sets into and out of Kafka. It works as a centralized data hub for simple data integration between databases, key-value stores, search indexes, and file systems.
KsqlDB : It is an event streaming database purpose-built to help developers create stream processing applications on top of Apache Kafka
Confluent Control Center : It is a web-based tool for managing and monitoring Apache Kafka. It provides a user interface that enables you to get a quick overview of cluster health, observe and control messages, topics, and Schema Registry, and to develop and run ksqlDB queries.
Installation of Confluent Platform:
Start the Confluent Platform using the Confluent CLI command below(Method 1)
1. If you plan to use the confluent local commands, you need to have the JDK version 1.8 or 1.11 on your local system.
(sudo apt-get install openjdk-11-jdk)
2. curl -O http://packages.confluent.io/archive/7.1/confluent-7.1.1.zip
3. unzip confluent-7.1.1.zip
( This path is added for confluent-hub connector as well as for confluent)
4. export CONFLUENT_HOME=~/confluent-7.1.1
5. export PATH=$CONFLUENT_HOME/bin:$PATH
6. echo $PATH
7. confluent local services start

8. Go to localhost:9021
Start the Confluent Platform Using Docker Compose Configuration Parameters (Method 2)
a.Zookeeper configuration

ZOOPKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT : Instructs ZooKeeper where to listen for connections by clients such as Apache Kafka.
b.Confluent Kafka configuration

KAFKA_BROKER_ID: Id number of the broker, if not set a default one will be generated
KAFKA_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME: Sets the name of the connection for internal communication
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: Instructs Kafka how to get in touch with ZooKeeper
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: This makes Kafka accessible from outside the container by advertising its location on the Docker host.
KAFKA_OFFSETS_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: This is required when you are running with a single-node cluster.
KAFKA_LISTENERS: Sets the ports where the server will receive connections for both OUTSIDE and INTERNAL listeners
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: Sets the type of encryption used for both OUTSIDE and INTERNAL connections
For this container, we have two mount points specified to store the kafka data and configuration at a local folder.
c.Confluent Schema Registry configuration

SCHEMA_REGISTRY_KAFKASTORE_CONNECTION_URL: A list of Kafka brokers to connect to.
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_HOST_NAME: The hostname advertised in ZooKeeper
d.Kafka Topics Generator configuration

The kafka-topic-generator is used only to create topics and do Kafka maintenance tasks on initialization, it does not stay running after the initial script
e.Kafka Connect configuration

CONNECT_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: A host: port pair for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster.
CONNECT_GROUP_ID: A unique string that identifies the Connect cluster group this worker belongs to.
CONNECT_CONFIG_STORAGE_TOPIC: The name of the topic in which to store connector and task configuration data.
CONNECT_OFFSET_STORAGE_TOPIC: The name of the topic in which to store offset data for connectors.
CONNECT_STATUS_STORAGE_TOPIC: The name of the topic in which to store state for connectors.
CONNECT_KEY_CONVERTER: Converter class for values. This controls the format of the data that will be written to Kafka for source connectors or read from Kafka for sink connectors.
CONNECT_VALUE_CONVERTER: Converter class for values. This controls the format of the data that will be written to Kafka for source connectors or read from Kafka for sink connectors.
f.Confluent Control Center configuration

CONTROL_CENTER_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: A host: port pair for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster.
CONTROL_CENTER_REPLICATION_FACTOR: Replication factor for Control Center topics.
CONTROL_CENTER_CONNECT_CLUSTER: To enable Control Center to interact with a Kafka Connect cluster
$ docker-compose -f confluent-kafka.yaml up -d
See, Control Center UI: localhost:9021

Create a topic in the Confluent Platform ( Topic created monitor-topic)

Apply changes in the configuration File of fluent bit (Add OUTPUT section for Kafka Integration with fluent-bit)

$ docker-compose -f fluent-bit.yaml up -d
All the system metrics (CPU, Disk, Memory) of server fetched by fluent-bit are sent to Kafka topic “monitor-topic”


Comments
Post a Comment